Data breaches caused businesses an average loss of $4.35 million in 2022.
Companies are constant targets for security breaches. Thus, prioritizing payment data security is critical.
Poor security can have disastrous consequences, including violating privacy laws and losing consumer trust.
EDI payments can help with security.
The question is: What are EDI payments?
I wrote this article to discuss this topic further. EDI payments, or Electronic Data Interchange payments, provide businesses with a secure and standardized method of exchanging payment information online.
This is the simple answer to “What is an EDI payment?” but there’s more you must know.
I’ll walk you through the EDI payment meaning and how businesses use it to streamline their payment operations.
Let’s begin.
What are EDI Payments?
EDI is Electronic Data Interchange, a communication system that lets businesses exchange encrypted information and documents.
In the context of payments, it refers to the electronic transfer of payment-related data.
Note: EDI isn’t a payment method. It’s a way of transmitting payment data from computer to computer, replacing paper-based documents.
I’ll discuss later why Amazon and Target use EDI solutions for processes and operations.
What Payment Data Does an EDI Message Contain?
The movement of funds, whether online or offline, requires several essential documents.
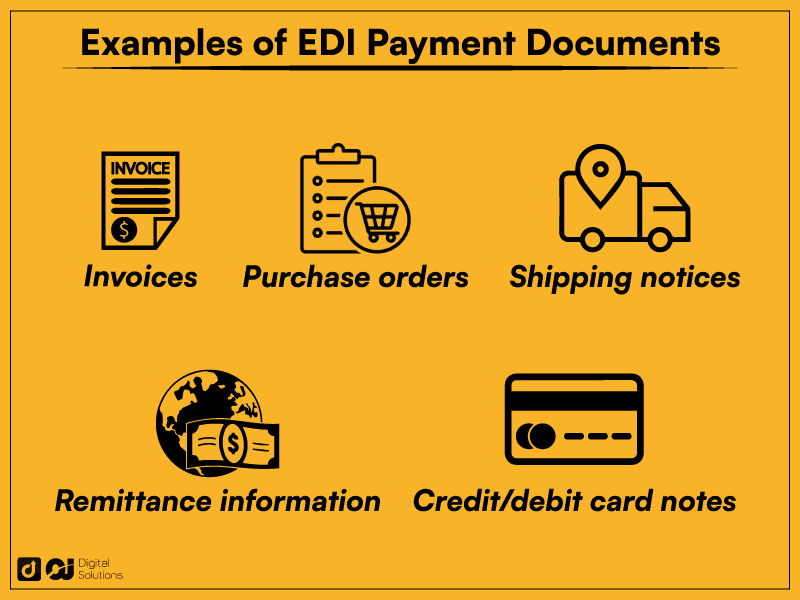
These EDI transaction documents include the following information about electronic payments.
Payer and payee details
Payment or funding method
Payment amount
Currency
Trace reference number
Credit or debit card information
The EDI format translates these details to enable computers to read and transmit data.
Electronic Data Interchange Payment Solutions
EDI payments have different types.
However, the two primary options are: 1) web and 2) direct.
Here’s how they differ and how you can choose which is right for your business.
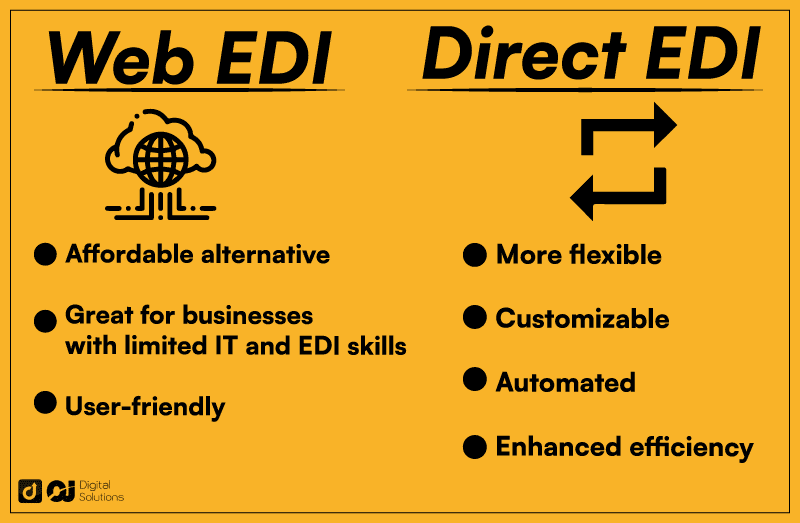
Web EDI
Web EDI is a cloud-based solution. It’s an affordable alternative for businesses without the resources to invest in extensive infrastructure.
With web EDI, all businesses need is an internet connection and a browser. Businesses can use a web-based interface to facilitate nationwide EDI payments.
The forms are online, making them accessible to any type of business.
Without in-house infrastructure, the software automatically converts payment data into EDI format, making it readable by your business partners’ internal systems.
Who’s It For?
Using web-based EDI solutions might be the better choice for small- to medium-sized businesses without complex requirements.
Companies with only occasional EDI payments may also find this solution more efficient.
Direct EDI or Point-to-Point
Direct EDI involves exchanging documents between two businesses. It uses a single communication network, connecting partners with the same protocol.
Businesses must set up an EDI infrastructure, which means investing in expensive software.
If you have more than two partners, you must create separate connections with each one.
Although it’s more expensive, it offers more flexibility and customization. Businesses, for example, can integrate their EDI system with their ERP and accounting systems.
Who’s It For?
Direct EDI payments allow businesses to automate several processes, enhancing efficiency and data accuracy. Larger businesses and suppliers often choose this option since they have more frequent and higher order volumes.
Which EDI Payment Type Is Better?
There’s no single best EDI solution.
The ideal solution for your business depends on these factors.
EDI requirements
Budget
Technical expertise
Technology structure
Scalability
Other types of EDI payments may suit your business requirements better.
Evaluate your needs before choosing the right electronic payment solution.
Manual vs. EDI Payment Process
How does EDI improve payment-related processes?
I’ll compare EDI to manual processing to give you a concrete idea of how EDI works.
Manual Payment Process
Trading partners communicate through traditional methods, like fax or mail. It can also be electronic if the buyer sends payment documents via email.
It involves at least one human on both sides.
The process can take days or weeks, from sending a purchase order to receiving an invoice.
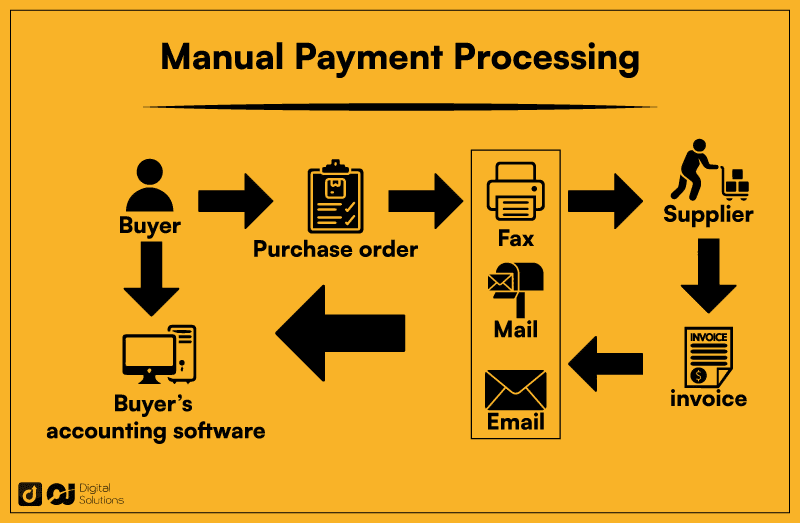
The manual process involves significant human interaction and paper documents. It takes extensive resources to complete the process, especially if more people are in the payment cycle.
Human involvement makes the process prone to errors, from tracking invoices to reconciling payments.
Manual data entry can lead to numerous mistakes, including typos and misinterpretations. These mistakes can increase the risk of disputes and payment cycle delays.
The time and effort it takes to complete the process and fix errors take attention away from more strategic activities. Businesses often spend more resources on manual payment processing than EDI payments.
EDI Payment Process
EDI offers a more streamlined approach to processing payments.
In a typical transaction, the buyer’s internal system communicates directly with the supplier’s internal system.
An EDI payment transaction doesn’t require human intervention because businesses can automate the steps in the payment cycle, including sending a purchase order, invoicing, and entering data into the EDI accounts payable system.
EDI has approximately half the steps required to complete a manual payment process.
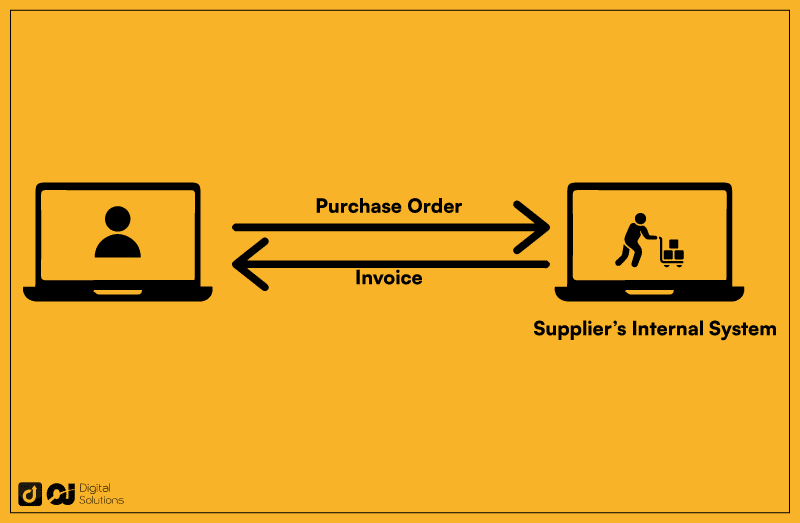
The process takes only a few hours, improving efficiency and reducing labor.
EDI allows vendors to quickly handle multiple transactions. It also reduces errors and improves cash flow by eliminating human intervention.
Why Businesses Should Use EDI Payments
EDI payments are ideal for businesses with multiple trading partners and a high volume of invoices and payments.
Ecommerce giants like Amazon and Walmart emphasize mandating EDI transactions with their trading partners.
However, even small retailers can use EDI.
Here are the benefits of using EDI.
Faster Payment Processing
EDI payments eliminate the need to wait for purchase orders and invoices.
Businesses don’t have to wait while vendors manually process their payments. They can get their supplies more quickly.
Vendors can receive payments more quickly and improve their cash flow. EDI payments can cut the processing time from weeks to days and days to real-time.
Improved Cash Flow
With faster processing, businesses can improve their cash flow, payment operations, and working capital management.
They can then use the additional resources to explore growth opportunities and invest in new initiatives. The streamlined accounting process allows businesses to free up staff to focus on more strategic tasks.
Improved Accuracy
No human intervention means no human errors. Removing humans from the equation can significantly reduce the risks of errors in payment details and order disputes, improving business operations.
Reduced Costs
EDI payments help businesses reduce various costs.
Automating the payment process helps reduce labor costs and other expenses on paper-based invoicing and processing.
EDI also reduces the costs of errors and disputes, saving businesses money and effort.
Improved Relationships with Suppliers
EDI is efficient and reliable, reducing the risk of disputes and delays, building trust, and strengthening the relationship between the parties.
Enhanced Security
EDI offers much better security than manual processing.
EDI uses secure communication protocols, protecting payment details from fraud or unauthorized access. Removing the human element from the whole process also secures sensitive information from bad actors.
Businesses can also enjoy the reduced risk of financial losses due to fraudulent activity. EDI also helps protect them from reputational damage.
Difference Between EDI, EFT, and ACH Payments
EFT, ACH, and EDI are all payment solutions.
However, they all differ in functionality and supported types of transactions.
Here’s a quick rundown of their differences.
EDI vs. ACH vs. EFT
EDI is simply a method of exchanging data electronically.
It’s a data format, not a payment method. However, companies use it to exchange payment data, like remittance information, bank details, and business invoices.
Business-to-business (B2B) transactions use EDI.
A buyer’s internal system submits a purchase order using a standard format, then the supplier’s internal system interprets the EDI document.
On the other hand, EFT (Electronic Funds Transfer) is a form of electronic payment, while ACH (Automated Clearing House) is a specific type of EFT.
EFT payments refer to any of these electronic fund transfers.
PIN transactions
Wire transfers
ATM withdrawal
Credit/debit card payments
ACH payments
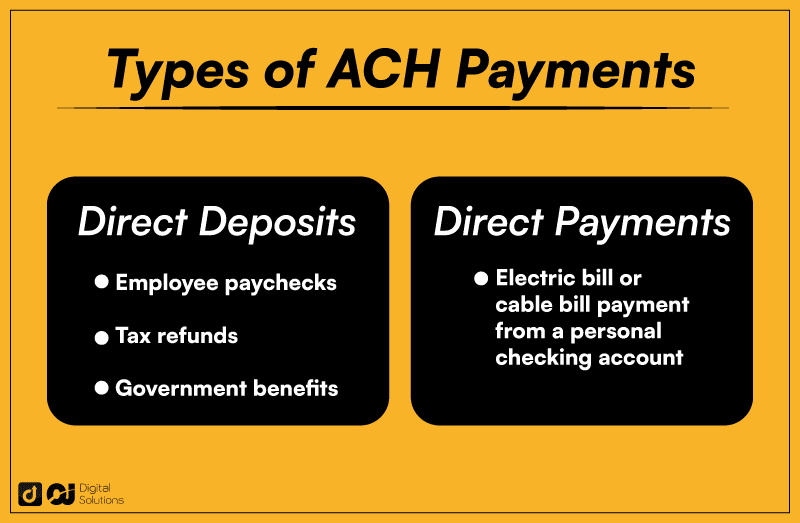
The National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA) manages the ACH network.
This network connects financial institutions, allowing individuals and businesses to move money from bank to bank.
Like EDI, ACH can include remittance information. EDI banking is also becoming commonplace.
You’ll likely hear EDI, ACH, and EFT as interchangeable terms, even from finance professionals. However, remember that these terms have specific meanings that can help you better understand payment processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why Did I Receive an EDI Payment (EDI Benefit Payment)?
You might see an EDI payment on bank statement documents, similar to an EFT or ACH payment. It means the institution processed the payment using EDI.
This is how an EDI payment may appear on your bank statement.
MDOL EDI Payment
Albert Genius EDI Payments
OSV EDI Payments (OneSource Virtual)
Direct Capital EDI Payments
DFC Global Corp EDI Payment
The information will vary depending on the financial institution.
For example, you might see a Raiser EDI payment on your bank statement if you were awarded a class action lawsuit payment.
What Industries Use EDI?
Here are some industries and businesses that use EDI.
Retail
Manufacturing
Healthcare
Transportation
Finance
Any business can use EDI to streamline its payment processes.
Is EDI Difficult to Implement?
Businesses new to electronic data interchange might find the implementation too complex.
However, many third-party EDI software and service providers, like Vanguard EDI payments solutions, can help you set up your payment system.
EDI Payment, Direct Deposit: Are They the Same?
EDI payment isn’t the same as a direct deposit.
EDI allows the transfer of payment-related information from one business to another.
Direct deposits transfer money into a bank account.
What Are Amazon EDI Payments?
Amazon also uses EDI payments to pay its suppliers and vendors. It streamlines the communication between their systems and the entire process of purchasing.
If you’re a vendor, consider Amazon EDI compliance. The platform offers a powerful solution that lets you enjoy all the benefits I mentioned in this article.
Can I Use EDI on Other Ecommerce Platforms?
Yes. Large retailers and platforms already use EDI to simplify payments for all parties. For example, you can integrate eBay EDI payments.
What Is EDI Billing?
EDI billing lets companies that send periodic billing statements to customers use electronic instead of paper billing.
For example, a power company can use EDI billing to send customers electronic bills, preventing paper waste.
The Bottom Line
EDI payments offer streamlined processing, enabling businesses to focus on strategic ventures instead. It lessens errors, reduces costs, and builds stronger supplier relationships.
A streamlined payment system can save you time, resources, and effort.
To further improve your small business efficiency, consider using the best payroll software for small businesses.